| Single
Dose Pharmacokinetics |
General
Disposition Parameters and Constants  |
Dose Amount
|
D
|
Fraction of dose absorbed
Used to correct dose amount for some oral dose calculations.
|
F
|
Exponential Summation
Expression for sum of 1st order kinetic terms.
|
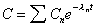
for n exponential terms
|
Y-Intercept
Coefficient of each exponential term. Note the sign of the
absorption coefficient is negative.
|
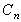 |
Slope
|
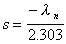 |
Rate constant
|
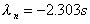 |
Elimination rate constant
|
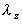 |
Half-life
|
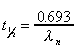 |
Descriptive
Curve Parameters  |
Cinitial
Initial concentration extrapolated to time zero for i.v. dose.
|
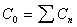 |
Tmax (obs)
Usually applies to oral doses only.
|
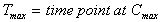 |
Cmax (calculated)
For biexponential oral data only.
|
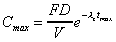
where V is Vd (area).
|
Tmax (calculated)
For biexponential oral data only.
|
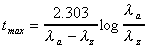
where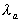 and and 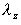 are
the apparent absorption and elimination rate constants, respectively. are
the apparent absorption and elimination rate constants, respectively.
|
Lag time
For biexponential oral data only.
|
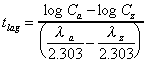
where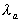 and and 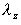 are
the apparent absorption and elimination rate constants, respectively. are
the apparent absorption and elimination rate constants, respectively.
|
Curve Area
Calculations  |
AUC(0-t) (obs area)
Trapezoid calculation of AUC using observed data points only
(not extrapolated to infinity). Useful when final concentration
values tend to exaggerate total AUC.
|
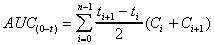
where n is the number of data points.
|
AUC (area)
Total AUC computed by combining AUC(0-t) with an extrapolated
value.
|
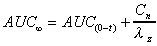
where 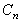 is
the last concentration. is
the last concentration.
|
AUC (expo)
Total AUC computed using exponential terms.
|
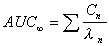 |
% of AUC (expo)
Percent each exponential term contributes to the total AUC.
|
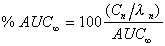 |
Statistical
Moment Calculations  |
AUMC (area)
Calculation of total area under the first-moment curve (plot
of Ct vs t) by combining trapezoid calculation
of AUMC(0-t) and extrapolated area.
|
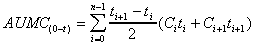
+ 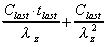
|
AUMC (expo)
Total AUMC computed using exponential terms.
|
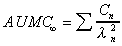 |
% of AUMC (expo)
Percent each exponential term contributes to the total AUMC.
|
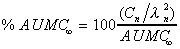 |
MRT (area)
Mean Residence Time calculated using trapezoid area calculations
extrapolated to infinity.
|
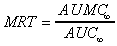
where both area terms use trapezoidal calculations
|
MRT (expo)
Mean Residence Time calculated using exponential terms.
|
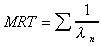 |
Volume of
Distribution Calculations  |
Vc (initial central compartment)
Apparent volume of the central compartment for i.v. doses
only.
|
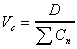 |
Vd (obs area)
Apparent volume of distribution based on AUC(0-t) trapezoid
calculation and elimination rate. Use when total AUC (area)
is exaggerated due to high terminal concentration values.
|
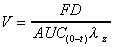 |
Vd (area)
Apparent volume of distribution based on trapezoid AUC (area)
and elimination rate. Applies mainly to i.v., but also to oral
if complete absorption (F=1) is assumed.
|
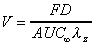 |
Vd (area) / kg
Apparent volume of distribution normalized by animal weight.
Uses same equation as Vd (area).
|
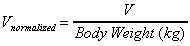 |
Vd (expo)
Apparent volume of distribution calculated from exponential
terms.
|
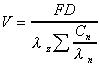
where 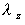 is
the elimination rate is
the elimination rate
|
Vss (area)
Apparent volume of distribution at steady state estimated
graphically from trapezoidal total area measurements. Applies
to iv dose.
|
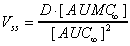 |
Vss (expo)
Apparent volume of distribution at steady state estimated
from exponential terms. Applies only after iv and assumes elimination
from central compartment.
|
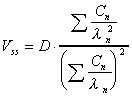 |
Systemic
Clearance Calculations  |
CL(sys) (obs area)
Systemic clearance based on AUC(0-t) trapezoid
calculation. Use when total AUC (area) is exaggerated due to
high last concentration.
|
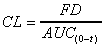 |
CL (area)
Systemic clearance based on trapezoid AUC (area). Applies
mainly to i.v. data. Limited to oral data only if complete absorption
(F=1) is assumed.
|
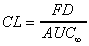 |
CL (area) / kg
Systemic clearance normalized by animal weight. Uses same
equation as CL (area).
|
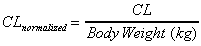 |
CL (expo)
Systemic clearance calculated using exponential terms.
|
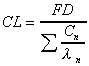 |
Half-life based on Vd and CL
Alternate calculation of half-life using Vd (area) and CL
(area). For i.v. data only.
|
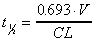 |
Two-compartment
Open Model Microconstants  |
k12
Microconstant calculated using exponentials. Applies to 2
compartment i.v. dose data only.
|
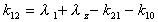 |
k21
Microconstant calculated using exponentials. Applies to 2
compartment i.v. dose data only.
|
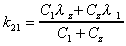 |
k10
Microconstant calculated using exponentials. Applies to 2
compartment i.v. dose data only.
|
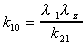 |
| Multiple
Intravenous Dose Pharmacokinetics |
General  |
Dose Interval (tau)
Time span between dosing intervals. Distinguish from time
after dose (t).
|
tau
Assume constant dose interval
|
First Dose
Concentration Calculations  |
C1(max)
Maximum concentration after first dose interval (tau).
Equal to Cinitial
|
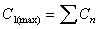 |
C1(min)
Minimum concentration at end of first dose interval (tau).
|
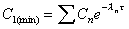 |
C1(ave)
Average concentration during first dose interval (tau).
|
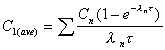 |
Prediction
of Steady State Parameters  |
Css(min)
Minimum concentration during any dosing interval at steady
state.
|
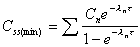 |
Css(min)
Minimum concentration during any dosing interval at steady
state. Included on graph.
|
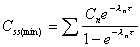 |
Css(max) - Css(min)
Difference between peak and trough concentration during steady
state.
|
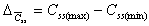 |
Css(ave)
Average concentration at steady state.
|
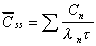 |
Css(ave) (area)
Average concentration at steady state calculated from trapezoidal
AUC data for a single dose.
|
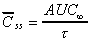 |
Accumulation
Factors  |
R based on Css(max)/C1(max)
Accumulation ratio based on maximum concentrations after first
dose and at steady state.
|
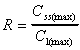 |
R based on Css(min)/C1(min)
Accumulation ratio based on minimum concentrations after first
dose and at steady state.
|
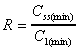 |
R based on Css(ave)/C1(ave)
Accumulation ratio based on average concentrations after first
dose and at steady state.
|
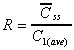 |
Time to
Reach Percent of Steady State  |
To reach 95% Css(ave)
Time required to reach 95% of average steady state concentration.
Assumes one-compartment characteristics apply.
|
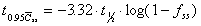
where 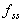 is
the fraction of the steady state concentration. is
the fraction of the steady state concentration.
|
To reach 99% Css(ave)
Time required to reach 95% of average steady state concentration.
Assumes one-compartment characteristics apply.
|
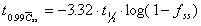
where 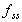 is
the fraction of the steady state concentration. is
the fraction of the steady state concentration.
|
Ad Hoc
Calculations  |
Calculated loading dose
Loading dose required to produce an immediate steady state
minimum concentration, Css(min).
|
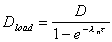 |
Total time through Nth dose
Total time elapsed between first dose (t=0) and specified
dose (N).
|
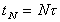 |
C(ave) during Nth dose
Average concentration during any dose interval (N). Becomes
Css(ave) when steady state reached.
|
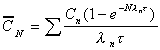 |
Fraction of Css(ave) after N doses
Fraction of the ultimate average steady state concentration
reached after N doses.
|
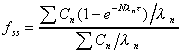
where 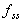 is
the fraction of the steady state concentration is
the fraction of the steady state concentration
|
Css at t after ss dose
Steady state concentration at any time (t) during a
dosing interval at steady state.
|
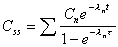 |
Conc. at any time and dose
Computes the concentration at any time during a dosing interval.
Enter both time (t) and dose interval (N).
|
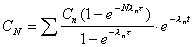 |
| Multiple
Oral Dose Pharmacokinetics |
General
and Graphing Functions  |
Dose Interval (tau)
Constant time span between dosing intervals. Distinguish from
time after dose (t).
|
(tau) Assumes equal dose intervals
|
Graphing Function
The graphing function is based on a mathematical generalization
of the graphical superimposition principle. It involves the
addition of a decay function (CN) to the initial
concentration (C1)at repeated time points for a progressive
series of doses (N). Assumes constant dose intervals during
the postdistribution phase.
|
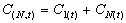
where
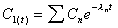
and
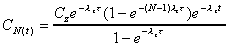
|
First Dose
Concentration Values  |
C1(max)
Observed maximum concentration taken from data set.
|
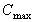 |
C1(min)
Minimum concentration at end of first dose interval (tau).
|
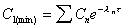 |
C1(ave)
Average concentration during first dose interval (tau).
|
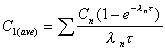 |
Prediction
of Steady State Parameters  |
Css(max)
Computed from a simplification of the graphing function to
a steady state form as shown. The Css(max) is evaluated as the
maximum concentration during the steady state dosing interval.
|
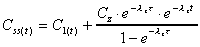
where
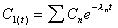
|
Css(min)
Computed using same steady state equation as Css(max) and
evaluating the minimum concentration during a steady state dose
interval.
|
Same as above.
|
Css(max) - Css(min)
Difference between peak and trough concentration during steady
state.
|
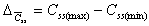 |
Css(ave)
Average concentration at steady state.
|
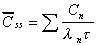 |
Css(ave) (area)
Average concentration at steady state calculated from trapezoidal
AUC data for a single dose.
|
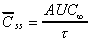 |
Accumulation
Factors  |
R based on Css(min)/C1(min)
Accumulation factor based on elimination rate constant.
|
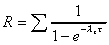 |
R based on Css(ave)/C1(ave)
Accumulation ratio based on average concentrations after first
dose and at steady state.
|
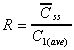 |
Additional
Oral Dose Calculations  |
Tmax (1st dose, observed)
Observed time of largest concentration value from data set.
|
 |
Tmax (1st dose, calculated)
Calculation of time at which maximum concentration occurs
after a single dose. Applies to 1-compartment characteristics,
but calculated also to illustrate magnitude for 2-compartments.
|
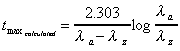
where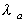 is
the absorption rate is
the absorption rate
and 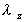 is
the elimination rate. is
the elimination rate.
|
Tmax(ss)
Calculation of time at which maximum concentration occurs
after dosing during steady state. Applies to 1-compartment characteristics,
but calculated also to illustrate magnitude for 2-compartments.
|
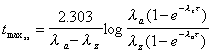
where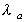 is
the absorption rate is
the absorption rate
and 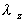 is
the elimination rate. is
the elimination rate.
|



